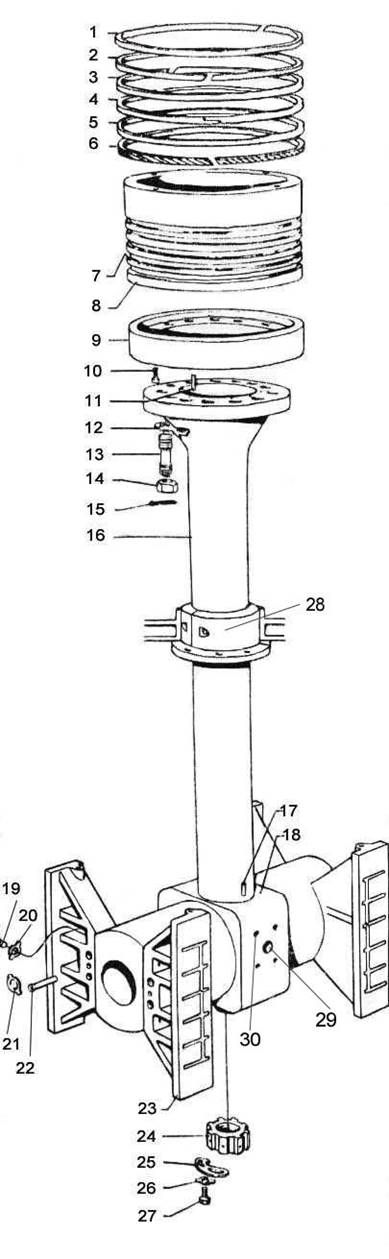
1. Segment (de piston);
2. Segment (de piston);
3. Segment (de piston);
4. Segment (de piston);
5. Segment (de piston);
6. Segment de ungere;
7. Canal pentru segment;
8. Piston – parte superioară;
9. Piston – parte inferioară;
10. Şurub;
11. Bolţ;
12. Şaibă de siguranţă (de blocare);
13. Prezon;
14. Piuliţă;
15. Bulon/bolţ cu cui spintecat (de siguranţă)
16. Tija pistonului;
17. Bolţ;
18. Cap de cruce;
19. Şurub;
20. Şaibă de siguranţă (de blocare);
21. Şaibă de siguranţă (de blocare);
22. Bolţ de ghidare;
23. Patina (capului de cruce);
24. Piuliţa tijei pistonului;
25. Şaibă de siguranţă (de blocare);
26. Şaibă de siguranţă (de blocare);
27. Şurub;
28. Presetupa tijei pistonului;
29. Intrarea uleiului de răcire al pistonului;
30. Ieşirea uleiului de răcire al pistonului;